By Paul Lindahl
•
February 18, 2022
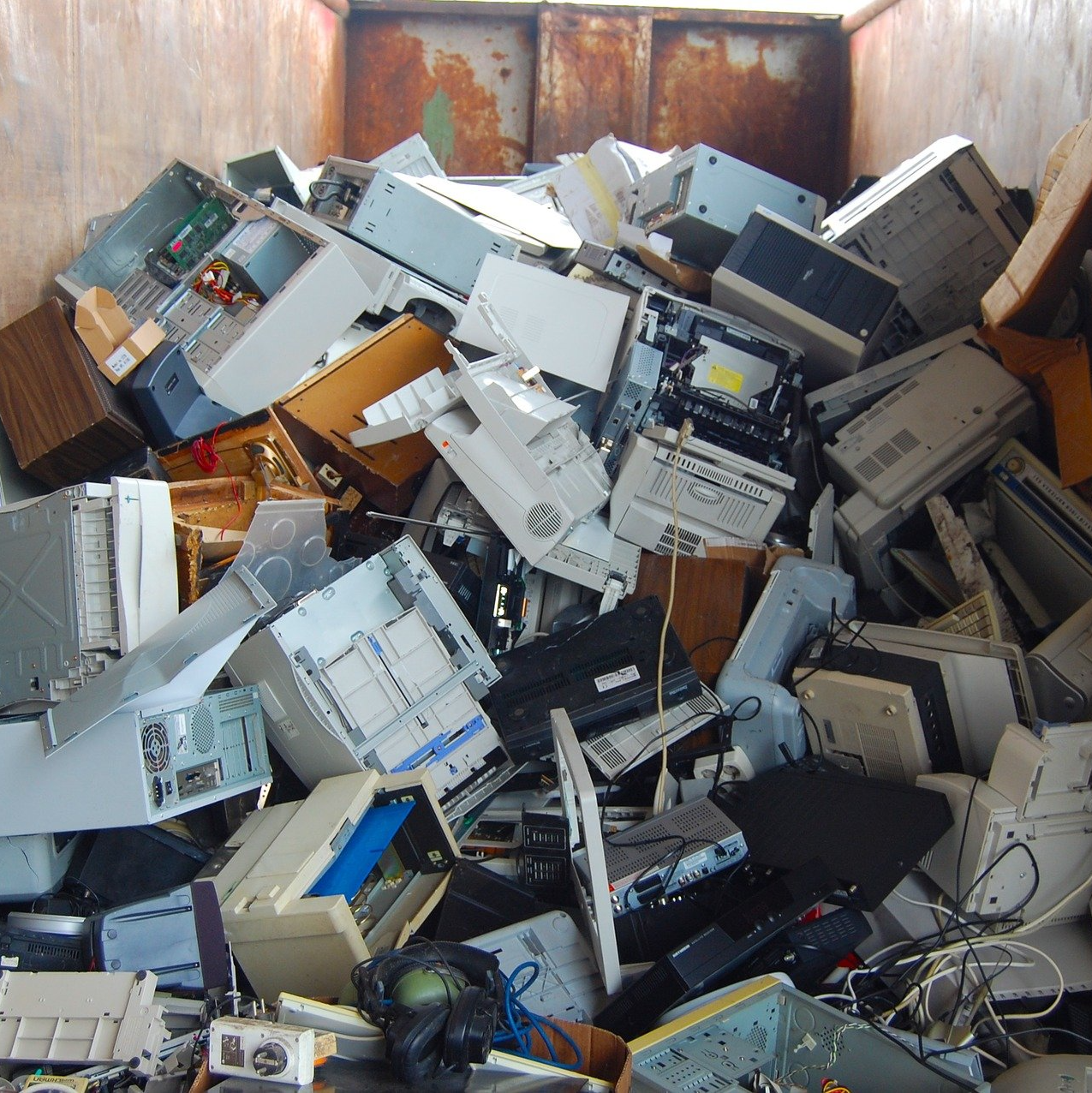
Electronic waste includes any white goods, consumer and business electronics, and information technology hardware that have reached the end of their useful life. As technology advances and organizations use cutting-edge equipment to gain a competitive advantage, there is a growing demand for proper e-waste disposal. The Global Importance of E-Waste Many of the components in these products are toxic and do not biodegrade easily, so e-waste has raised concerns. According to a survey, much e-waste is disposed of in an unsafe manner in developing countries, posing an environmental and health risk. According to the United Nations Environment Programme, illegal disposal can occur in the name of charitable donation (UNEP). Environmental Impact of Electronic Waste E-waste has the potential to be toxic and is not biodegradable. It builds up in the environment, which includes soil, air, water, and living things. E-waste-related air pollution has a greater impact on some animal species than others, potentially endangering these species as well as the biodiversity of certain chronically polluted areas. Air pollution can cause irreversible harm to ecosystems by degrading water quality, soil quality, and plant species over time. Furthermore, e-waste disposed of through open burning or other illegal methods (more common in developing countries) can contaminate wildlife, such as fish, which can be traded locally or globally. Types of Electronic Waste we Pick Up and Remove Fridges, freezers, and other cooling equipment. Computers, printers, fax machines and telecommunications equipment. Consumer electronic devices, cell phones and solar panels. Phone systems, phone cables, and networking cables. TVs, monitors, and big screens. LED bulbs, halogen lights. Vending machines. Water heaters. FAQ Electronic waste includes any white goods, consumer and business electronics, and information technology hardware that have reached the end of their useful life. As technology advances and organizations use cutting-edge equipment to gain a competitive advantage, there is a growing demand for proper e-waste disposal. The Global Importance of E-Waste Many of the components in these products are toxic and do not biodegrade easily, so e-waste has raised concerns. According to a survey, much e-waste is disposed of in an unsafe manner in developing countries, posing an environmental and health risk. According to the United Nations Environment Programme, illegal disposal can occur in the name of charitable donation (UNEP). Environmental Impact of Electronic Waste E-waste has the potential to be toxic and is not biodegradable. It builds up in the environment, which includes soil, air, water, and living things. E-waste-related air pollution has a greater impact on some animal species than others, potentially endangering these species as well as the biodiversity of certain chronically polluted areas. Air pollution can cause irreversible harm to ecosystems by degrading water quality, soil quality, and plant species over time. Furthermore, e-waste disposed of through open burning or other illegal methods (more common in developing countries) can contaminate wildlife, such as fish, which can be traded locally or globally. Types of Electronic Waste we Pick Up and Remove Fridges, freezers, and other cooling equipment. Computers, printers, fax machines and telecommunications equipment. Consumer electronic devices, cell phones and solar panels. Phone systems, phone cables, and networking cables. TVs, monitors, and big screens. LED bulbs, halogen lights. Vending machines. Water heaters. FAQ What are the potential dangers of disposing of old electronics? E-waste is a dangerous substance. Electronics can leak poisonous elements like mercury and lead over time, posing a risk to both the environment and humans. Controlling the threats can be as simple as donating your devices for reuse or recycling them at properly supervised facilities. Why is it important to dispose of electronic devices safely? Toxic chemicals and heavy metals are found in electronic devices. Chromium, cadmium, mercury, and lead can leak into the soil, damaging the air and waterways. Recycling this material saves landfill space. How can e-waste be disposed of ethically? Take them to an e-waste recycling center that specializes in this type of garbage. Find a reputable local organization that will recycle the item if there is no way to reuse or return it. There are many businesses that will accept old electronics; Recycle Now makes it simple to find one in your community. What happens if e-waste is not disposed of properly? Electronic products that are not properly disposed of having the potential to harm the environment. Exposure to environmental pollutants is projected to rise as more e-waste is disposed of in landfills, raising the risk of cancer and developmental and neurological diseases. What is e-waste give examples? Consumer electronics (TVs, mobile phones, DVD players, and so on) Office electronics (laptops, projectors, scanners, printers, copiers, and so on) Lighting devices (incandescent lamps, light-emitting diode (LED) lamps, compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) lamps, and so on) Power tools (Air compressor, Hammer Drill, etc.) White goods (fridges, stove, oven, washing machines and dryers) Electronic recliners and sofas Ways to Control Electronic Waste and Its Hazards Sell your old electronics. Donate old electronic devices Properly recycle and dispose of e-waste (Call us!) Repurpose or rethink Rather than purchasing, consider renting electronic equipment. Contact Us to Dispose of your Electronic Waste We will also help you with recycling and disposal options for electronic items if necessary. If you have any questions please contact us.